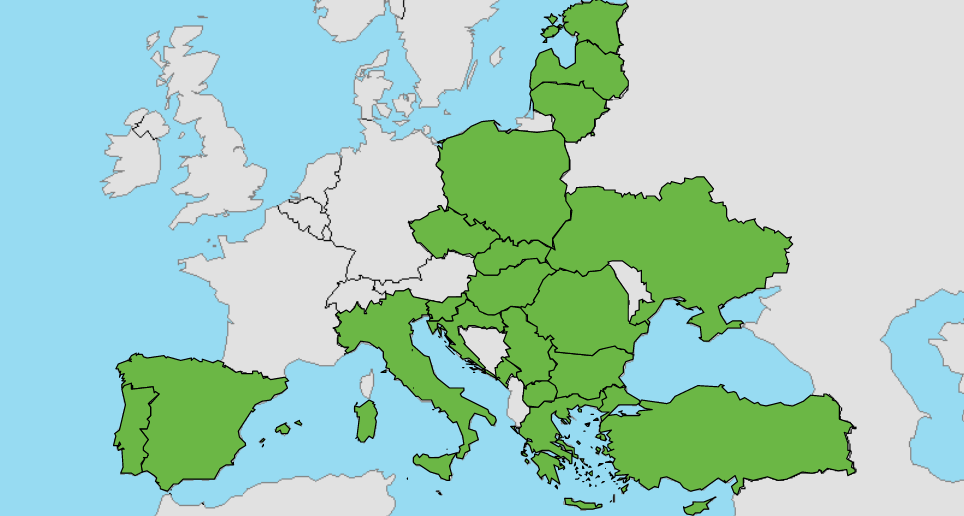
RIS countries are countries that benefit from the Regional Innovation Scheme within the EIT (European Institute of Innovation and Technology) funding scheme. The EIT RIS scheme was introduced in 2014 to advance the innovation performance of more countries and their regions across Europe, especially countries with moderate or modest innovation scores as defined by the European Innovation Scoreboard. Since its establishment, the EIT RIS has successfully lead to a significant expansion of EIT Community activities to more countries and regions across Europe, contributing to a pan-European spread of EIT Community engagement opportunities and networks.
Countries eligible to take part in the EIT RIS (2021-2024):
- EU Member States: Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Estonia, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain.
- Horizon Europe Associated Countries*: Montenegro, Republic of North Macedonia, Serbia, Turkey, Ukraine.
- Outermost Regions: Guadeloupe, French Guiana, Réunion, Martinique, Mayotte and Saint-Martin (France), the Azores and Madeira (Portugal), and the Canary Islands (Spain).
*These third countries, which are all listed in the European Innovation Scoreboard, will be fully eligible for the EIT RIS, following the successful conclusion of individual Horizon Europe Association Agreements.
Who can participate?
Any entity from a RIS eligible country or region can participate in EIT RIS activities. Through the EIT RIS, each EIT KIC will engage with local innovators – individuals such as students, researchers, entrepreneurs, as well as, organisations such as SMEs, universities, research labs, regions, NGOs and cities. The EIT KICs also involve the local players in education, business creation and acceleration activities, as well as innovation-driven research.
What are the EIT RIS objectives?
The overarching objective of the EIT RIS is to contribute to the advancement of the innovation performance of the targeted countries and their regions by strengthening the capacity of their innovation enablers and actors and linkages among them (such as business accelerators, incubators, start-ups, scale-ups, businesses including SMEs, agencies, educational and research institutions and their infrastructures, etc.) through the dissemination of the KTI approach, the cornerstone of the EIT intervention logic. RIS aims to enhance the innovation capacity in moderate and modest / emerging innovators Member States, eligible Horizon Europe Associated Countries and EU Outermost Regions.
RIS concentrates on capacity building activities and closer interactions between the local knowledge triangle innovation actors and their activities, it widens the participation in EIT Innovation Communities, including through RIS Hubs, and strengthens links to Smart Specialisation Strategies and leverage additional private and public funding, especially ESI Funding. The RIS budget is of 10-15% of the EIT grant that should be allocated to EIT RIS activities.
More specifically, during the 2021-2027 period, the EIT RIS shall aim to deliver on the following objectives:
- improve the innovation capacities of the local ecosystem, via capacity building activities and closer interactions between the local KT innovation actors (such as, clusters, networks, regional public authorities, Higher Education Institutions (HEIs), research organisations, Vocational Education and Training (VET) institutions, SMEs) and their activities;
- support the objective of attracting and facilitating the integration of potential new partners in the EIT KICs and link local innovation ecosystems to pan-European innovation ecosystems, including through the establishment of Co-Location Centres (CLCs) and RIS Hubs, as part of a “place-based” innovation approach;
- used as a bridge towards relevant Research and Innovation Smart Specialisation Strategies (RIS3s);
- leverage additional private and public funding, with particular attention to European Structural and Investment Funds (ESIF).
Source and more information on the EIT website.